Microscopy & Microtechniques
Temperature Controlled Stage used for the Investigation of Gold Deposits in Honduras
Jul 24 2012
Using a THMSG600 Linkam stage, scientists at the Department of Physics and Earth Science from the University of Parma are investigating gold deposits from the Lepaguare valley mining district, Honduras.
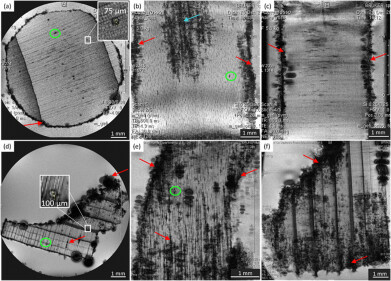
The Lepaguare is within a mountain belt that hosts several precious metal vein deposits and extends from Guatemala to Costa Rica through the Honduras region. These deposits mainly consist of gold and sulphide and are associated with thick quartz veins within pre-Mesozoic metamorphic rocks. Inside the veins, the quartz crystals are rich in fluid inclusions (FI) which can be studied to provide an understanding of the history of the gold deposits.
FI offer the possibility of reconstructing the environmental conditions (pressure, temperature, oxygen fugacity) and give information on the composition of the supercritical fluids in the environment during mineral formation.
These fluid inclusions have been studied using a THMSG600 Linkam stage to try to understand the composition of the fluids entrapped in quartz crystals. Using micro-thermometry and micro-Raman spectroscopy, scientists have investigated the physical and chemical conditions and chemical composition of the mineralising fluids. A Linkam THMSG600 stage (placed on the rotating stage of a transmitted optical light microscope) is used to take micro-thermometric measurements on the inclusions. Micro-thermometry consists of freezing runs to -196°C followed by heating runs up to 600°C, which test the composition of the fluids and mimic the conditions of their entrapment. Micro-thermometry indicates entrapment temperatures of mineralising fluids of 210-413°C and, associated with Raman spectra, the composition H2O-NaCl-KCl-CO2-CH4 for the mineralising fluids.
Due to temperature decrease and thermal contraction between mineral host and mineral fluid, they form daughter phases, which may be formed of one or more liquids, one vapour bubble, and possibly solid phases.
Emma Salvioli-Mariani, a researcher at the University of Parma, explained: "I am using the heating/freezing stage THMSG600 to understand the pressure and temperature conditions of mineral and rock formation, and to study fluid content of magma and the magma evolution. I find the possibility of programming the heating cycles with different ramps, the greater control on the heating and cooling rate and the ease of loading the sample just some of the advantages of using the Linkam stage."
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.6 Dec 2024
December 2024
Chromatography Articles - Sustainable chromatography: Embracing software for greener methods Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - Solving industry challenges for phosphorus containi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 22 2025 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 22 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jan 25 2025 San Diego, CA, USA
Jan 27 2025 Dubai, UAE
Jan 29 2025 Tokyo, Japan