-
 Professor Greg Neely and PhD student Tian Du in the Charles Perkins Centre University of Sydney. Photo Fiona Wolf-USYD-hires
Professor Greg Neely and PhD student Tian Du in the Charles Perkins Centre University of Sydney. Photo Fiona Wolf-USYD-hires -
-Liverpool-School-of-Tropical-Medicine-handling-a-snake.-Photo-credit-Ben-Gilbert.jpg) Professor Nicholas Casewell, (right) Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. Photo credit Ben Gilbert
Professor Nicholas Casewell, (right) Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. Photo credit Ben Gilbert
Research News
Researchers discover affordable antidote for cobra bites
Jul 19 2024
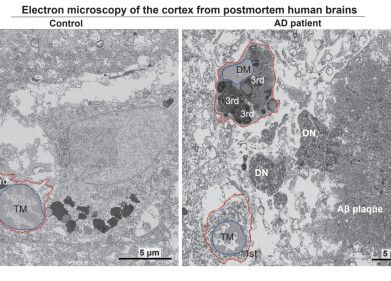
Scientists from the University of Sydney and Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine have discovered that heparin, a commonly used blood thinner, can be repurposed as an inexpensive antidote for cobra venom.
Cobras kill thousands and severely injure many more each year, with venom-induced necrosis often leading to amputation. Current antivenoms are costly and ineffective against local necrosis.
“Our discovery could drastically reduce necrosis injuries from cobra bites and might also slow the venom, improving survival rates,” said Professor Greg Neely, a corresponding author of the study from the Charles Perkins Centre and Faculty of Science at the University of Sydney.
Using CRISPR gene-editing technology, an international team identified ways to block cobra venom. They found that heparin and related drugs can stop the necrosis caused by bites.
Published in Science Translational Medicine, the study shows that heparin, an inexpensive and widely available drug, could be quickly implemented after successful human trials. “Heparin is a WHO-listed Essential Medicine and could become a cheap, safe, and effective treatment for cobra bites,” said lead author Tian Du, PhD student at the University of Sydney.
The team discovered that enzymes producing heparan and heparin are crucial for venom to cause necrosis. By flooding the bite site with ‘decoy’ heparin sulfate or related molecules, the antidote binds to and neutralises the venom toxins, preventing tissue damage.
Professor Nicholas Casewell from the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine highlighted the significance of this discovery for low- and middle-income countries, where snakebites are a major health issue. “Current antivenoms are largely ineffective against severe local envenoming, leading to significant disability,” he said.
Snakebites cause up to 138,000 deaths annually, with 400,000 more suffering long-term consequences. In parts of India and Africa, cobra species are responsible for many incidents.
The World Health Organization aims to halve the global burden of snakebites by 2030. Professor Neely hopes this new antidote will help achieve that goal and reduce death and injury in the world’s poorest communities.
The research team uses CRISPR technology to identify and block genetic targets of venoms. This approach also led to an antidote for box jellyfish venom in 2019.
Professor Casewell’s Centre for Snakebite Research & Interventions has over 50 years of expertise in improving antivenom treatments and understanding snake venom biology. The centre hosts leading experts and the UK’s largest collection of tropical venomous snakes.
More information online:
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.6 Dec 2024
December 2024
Chromatography Articles - Sustainable chromatography: Embracing software for greener methods Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - Solving industry challenges for phosphorus containi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 22 2025 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 22 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jan 25 2025 San Diego, CA, USA
Jan 27 2025 Dubai, UAE
Jan 29 2025 Tokyo, Japan