-
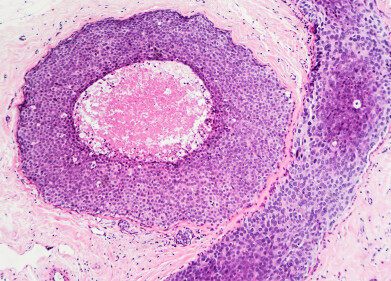
 “HepaRGTM Terminally Differentiated Human Hepatic Cells”
“HepaRGTM Terminally Differentiated Human Hepatic Cells”
Laboratory Products
Merck Millipore to Offer HepaRG™ Terminally Differentiated Human Hepatic Cells
Dec 01 2011
Merck Millipore will be the initial distributor of HepaRG™ human hepatic cells from Biopredic. HepaRG™ cells, derived from a hepatocellular carcinoma, are supplied as cryopreserved, terminally differentiated cells and express major liver specific functions including Cytochrome P450 enzymes and drug transporters.
HepaRG™ cells provide a number of advantages over primary hepatocytes and liver slices for characterization of the uptake, metabolism, and disposition of drug candidates, drug discovery, and high throughput screening. The supply of primary cells and tissue can be unpredictable and other transformed lines such as HepG2 have not gained widespread use due to loss of specific liver functions such as activity of the various Cytochrome P450 enzymes, thus impacting the proper assessment of toxicity.
With more than 900 drugs having been implicated in causing liver injury and toxicity, there is a need for more accurate prediction of hepatic cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in humans.
The challenges of hepatocyte-based in vitro toxicity testing have led pharmaceutical companies to rely heavily on animal models for preclinical metabolism and toxicity testing. But animal models also have limitations. Animal models may not be fully and reliably predictive of human toxicity, are low throughput, expensive, and raise ethical concerns for some.
Cost and throughput often relegate use of animal models to the later stages of preclinical development, after a company has invested significant resources and time in a lead compound. This delayed evaluation of toxicity contributes to the high failure rate of compounds in late stage preclinical testing, which is extremely costly.
Immortalized hepatocyte cell lines can be cultured indefinitely, which addresses the supply and variability issues associated with use of primary human hepatocytes. However, these cells display distinct differences from normal liver cells and may not exhibit normal cell behavior or response. For example, most cytochrome P450 enzymes are expressed only weakly in HepG2 cells compared to normal human hepatocytes.
Earlier, more effective assessment of drug candidate toxicity has the potential to reduce the attrition rate of drugs in later stages of development.
While in vitro human liver preparations offer the most pertinent models, availability and inter-donor variability are significant drawbacks and transformed cell lines may not be representative of in vivo conditions. In contrast, HepaRG™ cells reproducibly express the activities of drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters to facilitate ADME/tox studies.
For More Information >CLICK HERE<
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.6 Dec 2024
December 2024
Chromatography Articles - Sustainable chromatography: Embracing software for greener methods Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - Solving industry challenges for phosphorus containi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 22 2025 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 22 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jan 25 2025 San Diego, CA, USA
Jan 27 2025 Dubai, UAE
Jan 29 2025 Tokyo, Japan
.jpg)