Chromatography
Quality Control and Optimisation of Coating Processes using Ion Chromatography
Feb 02 2022
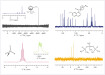
Surface finishing such as electroplating is one of the most important industrial processes to design products with dedicated physical, chemical, and electronic properties. Purity and composition of solutes, solvents, catalysts, and the electrolytic baths are a key requirement to achieve the desired properties, prevent damages and inferiority of the products by imbalances or contaminations. Impurities, even on an ultratrace level, can have detrimental effects for example on the electrical properties of integrated circuits and final products in the semiconductor industry. Therefore, Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI) stipulates for many basic chemicals and raw materials impurity levels in the low µg/L range. Ion chromatography (IC) is the ideal method for analysing ionic impurities, even in the ng/L range.
Impurities like fluoride, chloride, bromide, nitrite, nitrate, phosphate, or sulphate may alter the properties of a bath. Consequently, the plating properties are impaired or the semiconductor even damaged. Chemicals and raw materials used for process solutions, such as etching, plating, or cleaning solutions, need to be virtually free of such ionic impurities. IC, combined with Inline Matrix Elimination and Inline Preconcentration, is ideal to determine such impurities even in ultratraces.
Inline Matrix Elimination removes uncharged or oppositely charged matrix components (e.g., hydrogen peroxide), thus reducing sample preparation and improving the column lifetime. Additional combination with the intelligent Inline Preconcentration increases the measuring sensitivity, allowing the analysis of impurities in the ng/L range.
Example applications include:
- Trace anion and cation analysis in ultrapure water
- Trace anion analysis in acids
- Chloride and sulphate in tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH)
- Anionic impurities in hydrogen peroxide or organic solvents such as isopropanol
The robustness of the technique allows to handle almost all process solutions, such as etching, extracting, or rinsing solutions.
More information online
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.6 Dec 2024
December 2024
Chromatography Articles - Sustainable chromatography: Embracing software for greener methods Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - Solving industry challenges for phosphorus containi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 22 2025 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 22 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jan 25 2025 San Diego, CA, USA
Jan 27 2025 Dubai, UAE
Jan 29 2025 Tokyo, Japan