Chromatography
One Stationary Phase, Three Modes of Separation: Reversed Phase and Normal Phase Separations on the Same Column
Aug 05 2006
Author: Joseph J. Pesek, Maria T. Matyska on behalf of Unassigned Independent Article
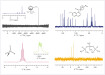
The most commonly used support material for HPLC packings are spherical, micro porous particles of silica and these are amorphous (i.e. non-crystalline) in nature. The surface of the silica particles shows poor homogeneity, being a mixture of silanols (Si-OH) of varying degrees of activity, and siloxane groups (Si-O-Si). This makes subsequent surface modifications to produce bonded phases greatly reliant on the nature of the base silica. Early silicas, made from sodium silica sols, were referred to as type A silicas. The more recent ’ultra pure’ silicas (exhibiting much lower levels of transition metal ions and better surface homogeneity - resulting in more reproducible and better chromatographic performance) , made from organic sols, are referred to as type B silicas. In this article Joe Pesek and Maria Matyska discuss a type C silica which is designed to reduce problems associated with types A&B silicas when modified.
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.6 Dec 2024
December 2024
Chromatography Articles - Sustainable chromatography: Embracing software for greener methods Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - Solving industry challenges for phosphorus containi...
View all digital editions
Events
Jan 22 2025 Tokyo, Japan
Jan 22 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jan 25 2025 San Diego, CA, USA
Jan 27 2025 Dubai, UAE
Jan 29 2025 Tokyo, Japan